Henry Irving on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sir Henry Irving (6 February 1838 – 13 October 1905), christened John Henry Brodribb, sometimes known as J. H. Irving, was an English stage actor in the
 His elder son,
His elder son,
 After a few years' schooling while living at Halsetown, near St Ives, Cornwall, Irving became a clerk to a firm of
After a few years' schooling while living at Halsetown, near St Ives, Cornwall, Irving became a clerk to a firm of  He gained recognition by degrees, and in 1866
He gained recognition by degrees, and in 1866
 In 1878, Irving entered into a partnership with actress
In 1878, Irving entered into a partnership with actress 
 After the production of Tennyson's ''The Cup'' and revivals of ''Othello'' (in which Irving played
After the production of Tennyson's ''The Cup'' and revivals of ''Othello'' (in which Irving played
 The chief remaining novelties at the Lyceum during Irving's term as sole manager (at the beginning of 1899 the theatre passed into the hands of a limited-liability company) were
The chief remaining novelties at the Lyceum during Irving's term as sole manager (at the beginning of 1899 the theatre passed into the hands of a limited-liability company) were  In 1898 Irving was
In 1898 Irving was
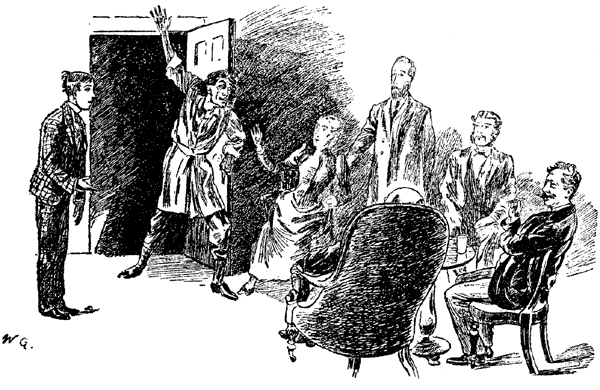 Irving's idiosyncratic style of acting and its effect on amateur players was mildly satirised in ''
Irving's idiosyncratic style of acting and its effect on amateur players was mildly satirised in ''
For he once was a Star of the highest degree--
He has acted with Irving, he's acted with
These verses appear in the lyrics of the homonymous song in Andrew Lloyd Webber's 1981 musical '' Cats''. In the 1963
''Personal Reminiscences of Henry Irving: Volume 1''
an
''Volume 2''
London : W. Heinemann, 1906. Scanned books via
Henry Irving, Actor and Manager: A Critical Study
London:Field & Tuer. * Beerbohm, Max. 1928. 'Henry Irving' in ''A Variety of Things.'' New York, Knopf. *Holroyd, Michael. 2008. ''A Strange Eventful History'', Farrar Straus Giroux, *Irving, Laurence. 1989. ''Henry Irving: The Actor and His World''. Lively Arts. * *
The Irving SocietyThe Henry Irving FoundationInformation about Irving at the PeoplePlay UK websiteNY Times article that includes information about Irving's American tour and the lease of the Lyceum to the American company at the same timeMy First "Reading" by Henry Irving, an article written by Irving about a personal experienceHenry Irving ''North American Theatre Online''
with bio and pics
Henry Irving-Ellen Terry tour correspondence, 1884-1896
held by the Billy Rose Theatre Division,
Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwardia ...
, known as an actor-manager
An actor-manager is a leading actor who sets up their own permanent theatrical company and manages the business, sometimes taking over a theatre to perform select plays in which they usually star. It is a method of theatrical production used co ...
because he took complete responsibility (supervision of sets, lighting, direction, casting, as well as playing the leading roles) for season after season at the West End’s Lyceum Theatre, establishing himself and his company as representative of English classical theatre. In 1895 he became the first actor to be awarded a knighthood
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of knighthood by a head of state (including the Pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church or the country, especially in a military capacity. Knighthood finds origins in the Gr ...
, indicating full acceptance into the higher circles of British society.
Life and career
Irving was born to aworking-class
The working class (or labouring class) comprises those engaged in manual-labour occupations or industrial work, who are remunerated via waged or salaried contracts. Working-class occupations (see also " Designation of workers by collar colou ...
family in Keinton Mandeville
Keinton Mandeville is a village and civil parish in Somerset, England, situated on top of Combe Hill, west of Castle Cary in the South Somerset district. The village has a population of 1,068. It is next to Barton St David.
Lakeview Quarry spe ...
in the county of Somerset
( en, All The People of Somerset)
, locator_map =
, coordinates =
, region = South West England
, established_date = Ancient
, established_by =
, preceded_by =
, origin =
, lord_lieutenant_office =Lord Lieutenant of Somerset
, lord_ ...
. W.H. Davies
William Henry Davies (3 July 1871 – 26 September 1940) was a Welsh poet and writer, who spent much of his life as a tramp or hobo in the United Kingdom and the United States, yet became one of the most popular poets of his time. His themes inc ...
, the celebrated poet, was a cousin. Irving spent his childhood living with his aunt, Mrs Penberthy, at Halsetown in Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic ...
. He competed in a recitation contest at a local Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's b ...
chapel where he was beaten by William Curnow, later the editor of ''The Sydney Morning Herald
''The Sydney Morning Herald'' (''SMH'') is a daily compact newspaper published in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, and owned by Nine. Founded in 1831 as the ''Sydney Herald'', the ''Herald'' is the oldest continuously published newspaper ...
''. He attended City Commercial School for two years before going to work in the office of a law firm at age 13. When he saw Samuel Phelps
Samuel Phelps (born 13 February 1804, Plymouth Dock (now Devonport), Plymouth, Devon, died 6 November 1878, Anson's Farm, Coopersale, near Epping, Essex) was an English actor and theatre manager. He is known for his productions of William ...
play Hamlet
''The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark'', often shortened to ''Hamlet'' (), is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare sometime between 1599 and 1601. It is Shakespeare's longest play, with 29,551 words. Set in Denmark, the play depicts ...
soon after this, he sought lessons, letters of introduction, and work in the Lyceum Theatre in Sunderland in 1856, labouring against great odds until his 1871 success in '' The Bells'' in London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
set him apart from all the rest.
He married Florence O'Callaghan on 15 July 1869 at St. Marylebone, London, but his personal life took second place to his professional life. On opening night of ''The Bells'', 25 November 1871, Florence, who was pregnant with their second child, criticised his profession: "Are you going on making a fool of yourself like this all your life?" Irving exited their carriage at Hyde Park Corner
Hyde Park Corner is between Knightsbridge, Belgravia and Mayfair in London, England. It primarily refers to its major road junction at the southeastern corner of Hyde Park, that was designed by Decimus Burton. Six streets converge at the j ...
, walked off into the night, and chose never to see her again. He maintained a discreet distance from his children as well, but became closer to them as they grew older. Florence Irving never divorced Irving, and once he had been knighted she styled herself "Lady Irving"; Irving never remarried.
 His elder son,
His elder son, Harry Brodribb Irving
Harry Brodribb Irving (5 August 1870 – 17 October 1919), was a British stage actor and actor-manager; the eldest son of Sir Henry Irving and his wife Florence ( née O'Callaghan), and father of designer Laurence Irving and actress Elizabeth ...
(1870–1919), usually known as "H B Irving", became a famous actor and later a theatre manager. His younger son, Laurence Irving (1871–1914), became a dramatist
A playwright or dramatist is a person who writes plays.
Etymology
The word "play" is from Middle English pleye, from Old English plæġ, pleġa, plæġa ("play, exercise; sport, game; drama, applause"). The word "wright" is an archaic English ...
and later drowned, with his wife Mabel Hackney
Mabel Lucy Hackney (1872 – 29 May 1914) was a British actress and the wife of the dramatist and actor Laurence Irving and daughter-in-law of the actor Henry Irving in whose company she acted before she joined that of her husband. She died alon ...
, in the sinking of the ''Empress of Ireland
RMS ''Empress of Ireland'' was a British-built ocean liner that sank near the mouth of the Saint Lawrence River in Canada following a collision in thick fog with the Norwegian Collier (ship), collier in the early hours of 29 May 1914. Althoug ...
''. H B married Dorothea Baird
Dorothea Baird (20 May 1875 – 24 September 1933) was an English stage and film actress.
Career
Her first stage appearance was with the Oxford University Dramatic Society in February 1894, when she played Iris in ''The Tempest''. She was ...
and they had a son, Laurence Irving (1897–1988), who became a well-known Hollywood art director and his grandfather's biographer.
In November 1882 Irving became a Freemason
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities ...
, being initiated into the prestigious Jerusalem Lodge No 197 in London. In 1887 he became a founder member and first Treasurer of the Savage Club Lodge No 2190, a Lodge associated with London's Savage Club
The Savage Club, founded in 1857, is a gentlemen's club in London, named after the poet, Richard Savage. Members are drawn from the fields of art, drama, law, literature, music or science.
History
The founding meeting of the Savage Club took ...
.
He eventually took over the management of the Lyceum Theatre and brought actress Ellen Terry
Dame Alice Ellen Terry, (27 February 184721 July 1928), was a leading English actress of the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Born into a family of actors, Terry began performing as a child, acting in Shakespeare plays in London, and tour ...
into partnership with him as Ophelia
Ophelia () is a character in William Shakespeare's drama '' Hamlet'' (1599–1601). She is a young noblewoman of Denmark, the daughter of Polonius, sister of Laertes and potential wife of Prince Hamlet, who, due to Hamlet's actions, ends u ...
to his Hamlet, Lady Macbeth to his Macbeth
''Macbeth'' (, full title ''The Tragedie of Macbeth'') is a tragedy by William Shakespeare. It is thought to have been first performed in 1606. It dramatises the damaging physical and psychological effects of political ambition on those w ...
, Portia to his Shylock, Beatrice to his Benedick, etc. Before joining the Lyceum, Terry had fled her first marriage and conceived two out-of-wedlock children with architect-designer Edward William Godwin
Edward William Godwin (26 May 1833, Bristol – 6 October 1886, London) was a progressive English architect-designer, who began his career working in the strongly polychromatic " Ruskinian Gothic" style of mid-Victorian Britain, inspired by ...
, but regardless of how much and how often her behavior defied the strict morality expected by her Victorian audiences, she somehow remained popular. It could be said that Irving found his family in his professional company, which included his ardent supporter and manager Bram Stoker and Terry's two illegitimate children, Teddy and Edy.
Whether Irving's long, spectacularly successful relationship with leading lady Ellen Terry
Dame Alice Ellen Terry, (27 February 184721 July 1928), was a leading English actress of the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Born into a family of actors, Terry began performing as a child, acting in Shakespeare plays in London, and tour ...
was romantic as well as professional has been the subject of much historical speculation. Most of their correspondence was lost or burned by her descendants. According to Michael Holroyd
Sir Michael de Courcy Fraser Holroyd (born 27 August 1935) is an English biographer.
Early life and education
Holroyd was born in London, the son of Basil de Courcy Fraser Holroyd (a descendant of Sir George Sowley Holroyd, Justice of the King' ...
's book about Irving and Terry, ''A Strange Eventful History'':
Terry's son Teddy, later known as Edward Gordon Craig
Edward Henry Gordon CraigSome sources give "Henry Edward Gordon Craig". (born Edward Godwin; 16 January 1872 – 29 July 1966), sometimes known as Gordon Craig, was an English modernist theatre practitioner; he worked as an actor, director a ...
, spent much of his childhood (from 1879, when he was 8, until 1897) indulged by Irving backstage at the Lyceum. Craig, who came to be regarded as something of a visionary for the theatre of the future, wrote an especially vivid, book-length tribute to Irving. ("Let me state at once, in clearest unmistakable terms, that I have never known of, or seen, or heard, a greater actor than was Irving.") George Bernard Shaw
George Bernard Shaw (26 July 1856 – 2 November 1950), known at his insistence simply as Bernard Shaw, was an Irish playwright, critic, polemicist and political activist. His influence on Western theatre, culture and politics extended from ...
, at the time a theatre critic who was jealous of Irving's connection to Ellen Terry (whom Shaw himself wanted in his own plays), conceded Irving's genius after Irving died.
Early career
 After a few years' schooling while living at Halsetown, near St Ives, Cornwall, Irving became a clerk to a firm of
After a few years' schooling while living at Halsetown, near St Ives, Cornwall, Irving became a clerk to a firm of East India
East India is a region of India consisting of the Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha
and West Bengal and also the union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The region roughly corresponds to the historical region of Magadh ...
merchants in London, but he soon gave up a commercial career for acting. On 29 September 1856 he made his first appearance at Sunderland as Gaston, Duke of Orleans, in Bulwer Lytton's play, ''Richelieu'', billed as Henry Irving. This name he eventually assumed by royal licence. When the inexperienced Irving got stage fright and was hissed off the stage the actor Samuel Johnson
Samuel Johnson (18 September 1709 – 13 December 1784), often called Dr Johnson, was an English writer who made lasting contributions as a poet, playwright, essayist, moralist, critic, biographer, editor and lexicographer. The ''Oxford ...
was among those who supported him with practical advice. Later in life Irving gave them all regular work when he formed his own Company at the Lyceum Theatre.
For 10 years, he went through an arduous training in various stock
In finance, stock (also capital stock) consists of all the shares by which ownership of a corporation or company is divided.Longman Business English Dictionary: "stock - ''especially AmE'' one of the shares into which ownership of a company ...
companies in Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
and the north of England, taking more than 500 parts.
 He gained recognition by degrees, and in 1866
He gained recognition by degrees, and in 1866 Ruth Herbert
Louisa Ruth Herbert (1831 – 1921) was a well-known Victorian-era English stage actress and model for the artist Dante Gabriel Rossetti.
Actress
She was the daughter of a West Country brass founder. She was also known as Mrs. Crabbe, having ma ...
engaged him as her leading man and sometime stage director at the St. James's Theatre
The St James's Theatre was in King Street, St James's, London. It opened in 1835 and was demolished in 1957. The theatre was conceived by and built for a popular singer, John Braham; it lost money and after three seasons he retired. A suc ...
, London, where she first played Doricourt in ''The Belle's Stratagem''. One piece that he directed there was W. S. Gilbert
Sir William Schwenck Gilbert (18 November 1836 – 29 May 1911) was an English dramatist, librettist, poet and illustrator best known for his collaboration with composer Arthur Sullivan, which produced fourteen comic operas. The most f ...
's first successful solo play, ''Dulcamara, or the Little Duck and the Great Quack
''Dulcamara, or the Little Duck and the Great Quack'', is one of the earliest plays written by W.S. Gilbert, his first solo stage success. The work is a musical burlesque of Donizetti's ''L'Elisir d'Amore'', and the music was arranged by Mr. Va ...
'' (1866) The next year he joined the company of the newly opened Queen's Theatre, where he acted with Charles Wyndham, J. L. Toole, Lionel Brough, John Clayton John Clayton may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Writing
*John Clayton (architect) (died 1861), English architect and writer
*John Bell Clayton and Martha Clayton, John Bell Clayton (c. 1907–1955), American writer
*John Clayton (sportswriter) ( ...
, Mr. and Mrs. Alfred Wigan
Alfred Sydney Wigan (24 March 1814Some sources say 24 March 1818 – 29 November 1878) was an English actor-manager who took part in the first Royal Command Performance before Queen Victoria on 28 December 1848.Gillan, DonA History of the Ro ...
, Ellen Terry
Dame Alice Ellen Terry, (27 February 184721 July 1928), was a leading English actress of the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Born into a family of actors, Terry began performing as a child, acting in Shakespeare plays in London, and tour ...
and Nellie Farren. This was followed by short engagements at the Haymarket Theatre, Drury Lane, and the Gaiety Theatre. In the spring of 1869, Irving was one of the original twelve members of The Lambs of London—assembled by John Hare as a social club for actors—and would be made an Honorary Lifetime member in 1883. He finally made his first conspicuous success as Digby Grant in James Albery
James Albery (4 May 1838 – 15 August 1889) was an English dramatist.
Life and career
Albery was born in London. On leaving school he entered an architect's office and started to write plays. His farce ''A Pretty Piece of Chiselling'' was ...
's ''Two Roses'', which was produced at the Vaudeville Theatre
The Vaudeville Theatre is a West End theatre on the Strand in the City of Westminster. As the name suggests, the theatre held mostly vaudeville shows and musical revues in its early days. It opened in 1870 and was rebuilt twice, although each ...
on 4 June 1870 and ran for a very successful 300 nights.
In 1871, Irving began his association with the Lyceum Theatre by an engagement under Bateman's management. The fortunes of the house were at a low ebb when the tide was turned by Irving's sudden success as Mathias in '' The Bells,'' a version of Erckmann-Chatrian
Erckmann-Chatrian was the name used by French authors Émile Erckmann (1822–1899) and Alexandre Chatrian (1826–1890), nearly all of whose works were jointly written.Mary Ellen Snodgrass, ''Encyclopedia of Gothic Literature''. New York, Facts ...
's '' Le Juif polonais'' by Leopold Lewis, a property which Irving had found for himself. The play ran for 150 nights, established Irving at the forefront of the British drama, and would prove a popular vehicle for Irving for the rest of his professional life.
With Bateman, Irving was seen in W. G. Wills' ''Charles I'' and ''Eugene Aram'', in ''Richelieu'', and in 1874 in ''Hamlet
''The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark'', often shortened to ''Hamlet'' (), is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare sometime between 1599 and 1601. It is Shakespeare's longest play, with 29,551 words. Set in Denmark, the play depicts ...
''. The unconventionality of this last performance, during a run of 200 nights, aroused keen discussion and singled him out as the most interesting English actor of his day. In 1875, again with Bateman, he was seen as the title character in ''Macbeth
''Macbeth'' (, full title ''The Tragedie of Macbeth'') is a tragedy by William Shakespeare. It is thought to have been first performed in 1606. It dramatises the damaging physical and psychological effects of political ambition on those w ...
''; in 1876 as Othello
''Othello'' (full title: ''The Tragedy of Othello, the Moor of Venice'') is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare, probably in 1603, set in the contemporary Ottoman–Venetian War (1570–1573) fought for the control of the Island of Cypru ...
, and as Philip in Alfred Lord Tennyson
Alfred Tennyson, 1st Baron Tennyson (6 August 1809 – 6 October 1892) was an English poet. He was the Poet Laureate during much of Queen Victoria's reign. In 1829, Tennyson was awarded the Chancellor's Gold Medal at Cambridge for one of his ...
's ''Queen Mary''; in 1877 in '' Richard III''; and in ''The Lyons Mail
''The Lyons Mail'' is a 1931 British historical mystery adventure film directed by Arthur Maude and starring John Martin Harvey, Norah Baring, and Ben Webster. It was based on the 1877 play '' The Lyons Mail'' by Charles Reade which in turn wa ...
''. During this time he became lifelong friends with Bram Stoker, who praised him in his review of ''Hamlet'' and thereafter joined Irving as the manager for the company.
Peak years
Ellen Terry
Dame Alice Ellen Terry, (27 February 184721 July 1928), was a leading English actress of the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Born into a family of actors, Terry began performing as a child, acting in Shakespeare plays in London, and tour ...
and re-opened the Lyceum under his own management. With Terry as Ophelia and Portia, he revived ''Hamlet
''The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark'', often shortened to ''Hamlet'' (), is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare sometime between 1599 and 1601. It is Shakespeare's longest play, with 29,551 words. Set in Denmark, the play depicts ...
'' and produced ''The Merchant of Venice
''The Merchant of Venice'' is a play by William Shakespeare, believed to have been written between 1596 and 1598. A merchant in Venice named Antonio defaults on a large loan provided by a Jewish moneylender, Shylock.
Although classified as ...
'' (1879). His Shylock was as much discussed as his Hamlet had been, the dignity with which he invested the vengeful Jew
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""Th ...
ish merchant marking a departure from the traditional interpretation of the role.

 After the production of Tennyson's ''The Cup'' and revivals of ''Othello'' (in which Irving played
After the production of Tennyson's ''The Cup'' and revivals of ''Othello'' (in which Irving played Iago
Iago () is a fictional character in Shakespeare's ''Othello'' (c. 1601–1604). Iago is the play's main antagonist, and Othello's standard-bearer. He is the husband of Emilia, who is in turn the attendant of Othello's wife Desdemona. Iago ha ...
to Edwin Booth
Edwin Thomas Booth (November 13, 1833 – June 7, 1893) was an American actor who toured throughout the United States and the major capitals of Europe, performing Shakespearean plays. In 1869, he founded Booth's Theatre in New York. Some theatri ...
's title character) and ''Romeo and Juliet
''Romeo and Juliet'' is a Shakespearean tragedy, tragedy written by William Shakespeare early in his career about the romance between two Italian youths from feuding families. It was among Shakespeare's most popular plays during his lifetim ...
'', there began a period at the Lyceum which had a potent effect on the English stage.
''Much Ado about Nothing
''Much Ado About Nothing'' is a comedy by William Shakespeare thought to have been written in 1598 and 1599.See textual notes to ''Much Ado About Nothing'' in ''The Norton Shakespeare'' ( W. W. Norton & Company, 1997 ) p. 1387 The play ...
'' (1882) was followed by ''Twelfth Night
''Twelfth Night'', or ''What You Will'' is a romantic comedy by William Shakespeare, believed to have been written around 1601–1602 as a Twelfth Night's entertainment for the close of the Christmas season. The play centres on the twins Vio ...
'' (1884); an adaptation of Goldsmith
A goldsmith is a Metalworking, metalworker who specializes in working with gold and other precious metals. Nowadays they mainly specialize in jewelry-making but historically, goldsmiths have also made cutlery, silverware, platter (dishware), pl ...
's ''Vicar of Wakefield
''The Vicar of Wakefield'', subtitled ''A Tale, Supposed to be written by Himself'', is a novel by Anglo-Irish writer Oliver Goldsmith (1728–1774). It was written from 1761 to 1762 and published in 1766. It was one of the most popular and w ...
'' by W. G. Wills (1885); ''Faust'' (1885); ''Macbeth'' (1888, with incidental music by Arthur Sullivan); ''The Dead Heart'', by Watts Phillips (1889); ''Ravenswood'' by Herman, and Merivales' dramatic version of Scott's '' Bride of Lammermoor'' (1890). Portrayals in 1892 of the characters of Wolsey
Thomas Wolsey ( – 29 November 1530) was an English statesman and Catholic bishop. When Henry VIII became King of England in 1509, Wolsey became the king's almoner. Wolsey's affairs prospered and by 1514 he had become the controlling figure ...
in '' Henry VIII'' and of the title character in ''King Lear
''King Lear'' is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare.
It is based on the mythological Leir of Britain. King Lear, in preparation for his old age, divides his power and land between two of his daughters. He becomes destitute and insane an ...
'' were followed in 1893 by a performance of Becket
''Becket or The Honour of God'' (french: Becket ou l'honneur de Dieu) is a 1959 play written in French by Jean Anouilh. It is a depiction of the conflict between Thomas Becket and King Henry II of England leading to Becket's assassination in 117 ...
in Tennyson
Alfred Tennyson, 1st Baron Tennyson (6 August 1809 – 6 October 1892) was an English poet. He was the Poet Laureate during much of Queen Victoria's reign. In 1829, Tennyson was awarded the Chancellor's Gold Medal at Cambridge for one of his ...
's play of the same name. During these years, too, Irving, with the whole Lyceum company, paid several successful visits to the United States and Canada, which were repeated in succeeding years. As Terry aged, there seemed to be fewer opportunities for her in his company; that was one reason she eventually left, moving on into less steady but nonetheless beloved stage work, including solo performances of Shakespeare's women.
Influence on Bram Stoker's ''Dracula''
From 1878,Bram Stoker
Abraham Stoker (8 November 1847 – 20 April 1912) was an Irish author who is celebrated for his 1897 Gothic horror novel '' Dracula''. During his lifetime, he was better known as the personal assistant of actor Sir Henry Irving and busine ...
worked for Irving as a business manager at the Lyceum. Stoker idolised Irving to the point that "As one contemporary remarked, 'To Bram, Irving is as a god, and can do no wrong.' In the considered judgment of one biographer, Stoker's friendship with Irving was 'the most important love relationship of his adult life.'" Irving, however, "… was a self-absorbed and profoundly manipulative man. He enjoyed cultivating rivalries between his followers, and to remain in his circle required constant, careful courting of his notoriously fickle affections." When Stoker began writing '' Dracula'', Irving was the chief inspiration for the title character
The title character in a narrative work is one who is named or referred to in the title of the work. In a performed work such as a play or film, the performer who plays the title character is said to have the title role of the piece. The title of ...
. In his 2002 paper for ''The American Historical Review
''The American Historical Review'' is a quarterly academic history journal and the official publication of the American Historical Association. It targets readers interested in all periods and facets of history and has often been described as the ...
'', "Buffalo Bill Meets Dracula: William F. Cody, Bram Stoker, and the Frontiers of Racial Decay", historian Louis S. Warren writes:
Later years
 The chief remaining novelties at the Lyceum during Irving's term as sole manager (at the beginning of 1899 the theatre passed into the hands of a limited-liability company) were
The chief remaining novelties at the Lyceum during Irving's term as sole manager (at the beginning of 1899 the theatre passed into the hands of a limited-liability company) were Arthur Conan Doyle
Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle (22 May 1859 – 7 July 1930) was a British writer and physician. He created the character Sherlock Holmes in 1887 for ''A Study in Scarlet'', the first of four novels and fifty-six short stories about Ho ...
's ''Waterloo'' (1894); J. Comyns Carr
Joseph William Comyns Carr (1 March 1849 – 12 December 1916), often referred to as J. Comyns Carr, was an English drama and art critic, gallery director, author, poet, playwright and theatre manager.
Beginning his career as an art critic, Car ...
's ''King Arthur'' in 1895; ''Cymbeline
''Cymbeline'' , also known as ''The Tragedie of Cymbeline'' or ''Cymbeline, King of Britain'', is a play by William Shakespeare set in Ancient Britain () and based on legends that formed part of the Matter of Britain concerning the early Celti ...
'', in which Irving played Iachimo, in 1896; Sardou's ''Madame Sans-Gene'' in 1897; and ''Peter the Great'', a play by Laurence Irving, the actor's second son, in 1898.
Irving received a death threat in 1899 from fellow actor (and murderer of William Terriss
William Terriss (20 February 1847 – 16 December 1897), born as William Charles James Lewin, was an English actor, known for his swashbuckling hero roles, such as Robin Hood, as well as parts in classic dramas and comedies. He was also a nota ...
) Richard Archer Prince. Terriss had been stabbed at the stage door of the Adelphi Theatre
The Adelphi Theatre is a West End theatre, located on the Strand in the City of Westminster, central London. The present building is the fourth on the site. The theatre has specialised in comedy and musical theatre, and today it is a receiv ...
in December 1897 and in the wake of his death, Prince was committed to Broadmoor Criminal Lunatic Asylum
Broadmoor Hospital is a high-security psychiatric hospital in Crowthorne, Berkshire, England. It is the oldest of the three high-security psychiatric hospitals in England, the other two being Ashworth Hospital near Liverpool and Rampton Secur ...
. Irving was critical of the unusually lenient sentence, remarking "Terriss was an actor, so his murderer will not be executed." Two years later, Prince had found Irving's home address and threatened to murder him "when he gets out". Irving was advised to submit the letter to the Home Office to ensure Prince's continued incarceration, which Irving declined to do.
 In 1898 Irving was
In 1898 Irving was Rede Lecturer
The Sir Robert Rede's Lecturer is an annual appointment to give a public lecture, the Sir Robert Rede's Lecture (usually Rede Lecture) at the University of Cambridge. It is named for Robert Rede, Sir Robert Rede, who was Chief Justice of the Common ...
at the University of Cambridge
, mottoeng = Literal: From here, light and sacred draughts.
Non literal: From this place, we gain enlightenment and precious knowledge.
, established =
, other_name = The Chancellor, Masters and Schola ...
. The new regime at the Lyceum was signalled by the production of Sardou's '' Robespierre'' in 1899, in which Irving reappeared after a serious illness, and in 1901 by an elaborate revival of ''Coriolanus
''Coriolanus'' ( or ) is a tragedy by William Shakespeare, believed to have been written between 1605 and 1608. The play is based on the life of the legendary Roman leader Caius Marcius Coriolanus. Shakespeare worked on it during the same ye ...
''. Irving's only subsequent production in London was as Sardou's ''Dante
Dante Alighieri (; – 14 September 1321), probably baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri and often referred to as Dante (, ), was an Italian poet, writer and philosopher. His ''Divine Comedy'', originally called (modern Italian: '' ...
'' (1903) at the Drury Lane.
On 13 October 1905, at 67 years old, Irving was taking part in a performance while on tour in Bradford
Bradford is a city and the administrative centre of the City of Bradford district in West Yorkshire, England. The city is in the Pennines' eastern foothills on the banks of the Bradford Beck. Bradford had a population of 349,561 at the 2011 ...
, when he suffered a stroke. He was taken to the lobby of the Midland Hotel, Bradford
The Midland Hotel is a 90- bedroom three- star Victorian hotel in Bradford city centre, owned and managed by London-based Peel Hotels.
The architect was Charles Trubshaw, who was contracted to design many railway stations for Midland Railway ...
, where he died shortly afterwards. His death was described by Thomas Anstey Guthrie
Thomas Anstey Guthrie (8 August 1856 – 10 March 1934) was an English author (writing as F. Anstey), most noted for his comic novel '' Vice Versa'' about a boarding-school boy and his father exchanging identities. His reputation was confirmed ...
in his 'Long Retrospect':
The chair that he was sitting in when he died is now at the Garrick Club
The Garrick Club is a gentlemen's club in the heart of London founded in 1831. It is one of the oldest members' clubs in the world and, since its inception, has catered to members such as Charles Kean, Henry Irving, Herbert Beerbohm Tree, Ar ...
. He was cremated and his ashes buried in Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the United ...
, thereby becoming the first person ever to be cremated prior to interment at Westminster.
There is a statue of him near the National Portrait Gallery in London. That statue, as well as the influence of Irving himself, plays an important part in the Robertson Davies
William Robertson Davies (28 August 1913 – 2 December 1995) was a Canadian novelist, playwright, critic, journalist, and professor. He was one of Canada's best known and most popular authors and one of its most distinguished " men of letters" ...
novel '' World of Wonders''. The Irving Memorial Garden was opened on 19 July 1951 by Laurence Olivier
Laurence Kerr Olivier, Baron Olivier (; 22 May 1907 – 11 July 1989) was an English actor and director who, along with his contemporaries Ralph Richardson and John Gielgud, was one of a trio of male actors who dominated the Theatre of the U ...
.
Legacy
Both on and off the stage, Irving always maintained a high ideal of his profession, and in 1895 he received aknighthood
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of knighthood by a head of state (including the Pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church or the country, especially in a military capacity. Knighthood finds origins in the Gr ...
(first offered in 1883), the first ever accorded an actor. He was also the recipient of honorary degrees from the universities of Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of th ...
(LL.D
Legum Doctor (Latin: “teacher of the laws”) (LL.D.) or, in English, Doctor of Laws, is a doctorate-level academic degree in law or an honorary degree, depending on the jurisdiction. The double “L” in the abbreviation refers to the earl ...
1892), Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
( Litt.D 1898), and Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated popul ...
(LL.D
Legum Doctor (Latin: “teacher of the laws”) (LL.D.) or, in English, Doctor of Laws, is a doctorate-level academic degree in law or an honorary degree, depending on the jurisdiction. The double “L” in the abbreviation refers to the earl ...
1899). He also received the Komthur Cross, 2nd class, of the Saxe-Ernestine House Order
The Saxe-Ernestine House Order (german: link=yes, Sachsen-Ernestinischer Hausorden)Hausorden
Herz ...
of Herz ...
Saxe-Coburg-Gotha
Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (german: Sachsen-Coburg und Gotha), or Saxe-Coburg-Gotha (german: Sachsen-Coburg-Gotha, links=no ), was an Ernestine, Thuringian duchy ruled by a branch of the House of Wettin, consisting of territories in the present- ...
and Saxe-Meiningen
Saxe-Meiningen (; german: Sachsen-Meiningen ) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine line of the Wettin dynasty, located in the southwest of the present-day German state of Thuringia.
Established in 1681, by partition of the Ernest ...
.
His acting divided critics; opinions differed as to the extent to which his mannerisms of voice and deportment interfered with or assisted the expression of his ideas.
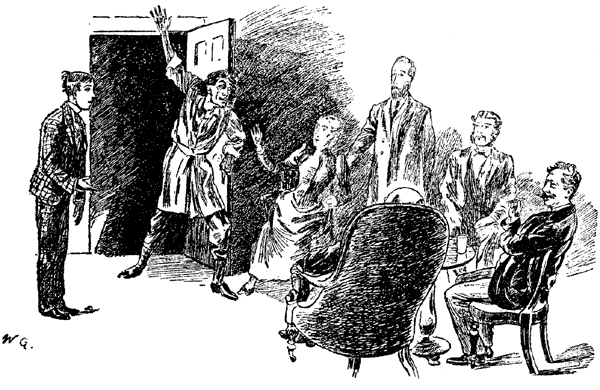 Irving's idiosyncratic style of acting and its effect on amateur players was mildly satirised in ''
Irving's idiosyncratic style of acting and its effect on amateur players was mildly satirised in ''The Diary of a Nobody
''The Diary of a Nobody'' is an English comic novel written by the brothers George and Weedon Grossmith, with illustrations by the latter. It originated as an intermittent serial in ''Punch'' magazine in 1888–89 and first appeared in book for ...
''. Mr Pooter's son brings Mr Burwin-Fosselton of the Holloway Comedians to supper, a young man who entirely monopolised the conversation, and:
"...who not only looked rather like Mr Irving but seemed to imagine he ''was'' the celebrated actor... he began doing the Irving business all through supper. He sank so low down in his chair that his chin was almost on a level with the table, and twice he kicked Carrie under the table, upset his wine, and flashed a knife uncomfortably near Gowing's face."In T. S. Eliot's poem, " Gus: The Theatre Cat" (ca. 1939), the title character's old age and theatrical distinction are expressed in the couplet:
For he once was a Star of the highest degree--
He has acted with Irving, he's acted with
Tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are ...
.These verses appear in the lyrics of the homonymous song in Andrew Lloyd Webber's 1981 musical '' Cats''. In the 1963
West End musical
West End theatre is mainstream professional theatre staged in the large theatres in and near the West End of London.Christopher Innes, "West End" in ''The Cambridge Guide to Theatre'' (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1998), pp. 1194–1 ...
comedy ''Half a Sixpence
''Half a Sixpence'' is a 1963 musical comedy based on the 1905 novel ''Kipps'' by H. G. Wells, with music and lyrics by David Heneker and a book by Beverley Cross. It was written as a vehicle for British pop star Tommy Steele.
Background
...
'' the actor Chitterlow does an impression of Irving in '' The Bells''. Percy French
William Percy French (1 May 1854 – 24 January 1920) was an Irish songwriter, author, poet, entertainer and painter.
Life
French was born at Clooneyquinn House, near Tulsk, County Roscommon, the son of an Anglo-Irish landlord, Christopher F ...
's burlesque heroic poem "Abdul Abulbul Amir
"Abdul Abulbul Amir" is the most common name for a music-hall song written in 1877 (during the Russo-Turkish War) under the title "Abdulla Bulbul Ameer" by Irish songwriter Percy French, and subsequently altered and popularized by a variety of o ...
" lists among the mock-heroic attributes of Abdul's adversary, the Russian Count Ivan Skavinsky Skavar, that "he could imitate Irving". In the 1995 film '' A Midwinter's Tale'' by Kenneth Branagh
Sir Kenneth Charles Branagh (; born 10 December 1960) is a British actor and filmmaker. Branagh trained at the Royal Academy of Dramatic Art in London and has served as its president since 2015. He has won an Academy Award, four BAFTAs (plus ...
, two actors discuss Irving, and one of them, Richard Briers
Richard David Briers (14 January 1934 – 17 February 2013) was an English actor whose five-decade career encompassed film, radio, stage and television.
Briers first came to prominence as George Starling in ''Marriage Lines'' (1961–66), but ...
does an imitation of his speech. In the play ''The Woman in Black
''The Woman in Black'' is a 1983 gothic horror novel by English writer Susan Hill. The plot concerns a mysterious spectre that haunts a small English town. A television film based on the story, also called '' The Woman in Black'', was produced ...
'', set in the Victorian era, the actor playing Kipps tells Kipps 'We'll make an Irving of you yet,' in Act 1, as Kipps is not a very good actor due to his inexperience.
In the political sitcom ''Yes, Prime Minister
''Yes Minister'' is a British political satire sitcom written by Antony Jay and Jonathan Lynn. Comprising three seven-episode series, it was first transmitted on BBC2 from 1980 to 1984. A sequel, ''Yes, Prime Minister'', ran for 16 episodes fro ...
'' (sequel to ''Yes, Minister
''Yes Minister'' is a British political satire sitcom written by Antony Jay and Jonathan Lynn. Comprising three seven-episode series, it was first transmitted on BBC2 from 1980 to 1984. A sequel, ''Yes, Prime Minister'', ran for 16 episodes fr ...
''), in the episode "The Patron of the Arts", first aired on 14 January 1988, the Prime Minister is asked what was the last play he'd seen, and replies "Hamlet." When asked "Whose?" — specifically, who played Hamlet, not who wrote it — he is unable to remember and is prompted with the suggestion "Henry Irving?" to audience laughter.
Biography
In 1906,Bram Stoker
Abraham Stoker (8 November 1847 – 20 April 1912) was an Irish author who is celebrated for his 1897 Gothic horror novel '' Dracula''. During his lifetime, he was better known as the personal assistant of actor Sir Henry Irving and busine ...
published a two-volume biography about Irving called '' Personal Reminiscences of Henry Irving''.Stoker, Bram (1906). Personal Reminiscences of Henry Irving. A complete PDF version of the book can be downloaded from Bram Stoker Online. Retrieved from .
See also
* Irving FamilyNotes
References
Further reading
* * Stoker, Bram''Personal Reminiscences of Henry Irving: Volume 1''
an
''Volume 2''
London : W. Heinemann, 1906. Scanned books via
Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, software applications/games, music, ...
.
* Archer, William 1885Henry Irving, Actor and Manager: A Critical Study
London:Field & Tuer. * Beerbohm, Max. 1928. 'Henry Irving' in ''A Variety of Things.'' New York, Knopf. *Holroyd, Michael. 2008. ''A Strange Eventful History'', Farrar Straus Giroux, *Irving, Laurence. 1989. ''Henry Irving: The Actor and His World''. Lively Arts. * *
External links
The Irving Society
with bio and pics
Henry Irving-Ellen Terry tour correspondence, 1884-1896
held by the Billy Rose Theatre Division,
New York Public Library for the Performing Arts
The New York Public Library for the Performing Arts, Dorothy and Lewis B. Cullman Center, at 40 Lincoln Center Plaza, is located in Manhattan, New York City, at the Lincoln Center for the Performing Arts on the Upper West Side, between the Metro ...
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Irving, Henry
1838 births
1905 deaths
English male stage actors
English male Shakespearean actors
19th-century English male actors
20th-century English male actors
19th-century theatre
Actor-managers
Knights Bachelor
Actors awarded knighthoods
English people of Cornish descent
People from South Somerset (district)
Burials at Westminster Abbey
Freemasons of the United Grand Lodge of England
19th-century theatre managers
20th-century theatre managers
Members of The Lambs Club